First Female Parliamentarian [279]
Mobile Teledensity 2006 [327]
Regional Energy Consumption and GDP [331]

Regional energy consumption (red horizontal bars) is correlated with vertical bar graphs indicating GDP (Gross Domestic Product) figures. Arrows indicate the rate of increasing consumption. China is currently the world's largest coal consumer and is projected to be the largest energy consumer by 2023.
Car-free Countries [325]
Nuclear Energy Dependency [162-4]
CO2 Spiral [30]
Oil and Coal Reserves [323]
Chemical and Energy Companies vs. Country [324]
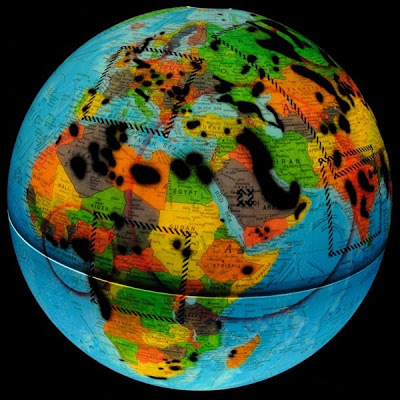
Global Warming - Greenhouse Contributors [293]
Japanese Empire (Dai-tō-a Kyōeiken) [304]

The concept of a Greater East Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere ( 大東亜共栄圏 Dai-tō-a Kyōeiken) was an Japanese attempt to create a Great East Asia free of Western Colonialism. The concept was also used to justify Japanese military conquests during the Great Asia War or Pacific War (roughly corresponding to WWII and preceding conflicts 1937 to 1945).
Fuel Sources, Consumption, and Prices [177]
Literacy [330]
Starting a Business [299]

The Cost and Capital Required to Start a Business.
In many countries the cost of procedures and the minimum capital required to start a business are so high that setting up a firm legally is all but impossible for most entrepreneurs. In Angola, for instance, the cost of starting a business is almost 450 percent of income per capita, and the minimum capital required is close to 500 percent.
On the globe, countries are removed from their actual geographic location and positioned on a grid. Along the black longitude line, countries are arranged according to the cost required to start a business; the cost, as a percentage of income per capita, increases from north to south. Along the red latitude line, countries are arranged according to the capital required to start a business; the capital, as a percentage of income per capita, increases from west to east. (For some very large countries, the exact position on the grid is indicated by a bright dot.) The farther north and west a country appears on the grid, the more affordable it is to start a business.
Night [41]

The military objectives of the US Air Force Defense Meteorological Satellite Program have created an aesthetic byproduct — a composite photo of the planet, taken during nighttime hours. More than 99% of these representations of actual light sources are indications of human activity on the planet. For example, this image includes more than a million man-made fires, most of them in the Third World, chiefly propagated for agricultural purposes. Population centers are easily identified; however, the amount of light represented here is not necessarily proportional to the population size. Imbalances arise due to unequal electrical consumption. Japanese consume 15 times as much electricity as Chinese per capita, and Americans consume 21/2 times more than Japanese do. This image also illustrates light pollution, a condition only astronomers have complained about so far.
One Taiwan Policy [266]
Export Impediments [296]

Every country requires official approval before exporters can ship their products abroad. However, requiring many approvals increases the risk of corruption and delays. While the world average is around 11 signatures required for export, countries in Sub-Saharan Africa require nearly double that number, and some require four times as many. In contrast, OECD countries require an average of only about three signatures. “Signatures required for export” is a sub-indicator of the IFC/World Bank’s “Doing Business” ranking (www.doingbusiness.org). On the globe, each check mark represents five signatures required (check marks are sized to fit the available space).
Carbon Emissions Trading [283]
Indicated are countries that have signed and ratified the Kyoto Protocol, and are thus eligible for participation in carbon emissions trading. Countries emitting levels of CO2 over 100,000 Gg (gigagrams) are designated by lengths of black bars corresponding to their emission levels. Thick bars indicate twice the amount thin bars do.
3 Hour US Air Force Range [241]
South - North and South - South Investment Flows [294]


Cross-border trade is a key element in private sector development. Trade between emerging market countries, also called South-South trade, more than tripled between 1995 and 2003, rising from $15 billion to $46 billion. Trade from the South to the North also grew substantially, reaching $7 billion in 2003 (World Bank estimates).
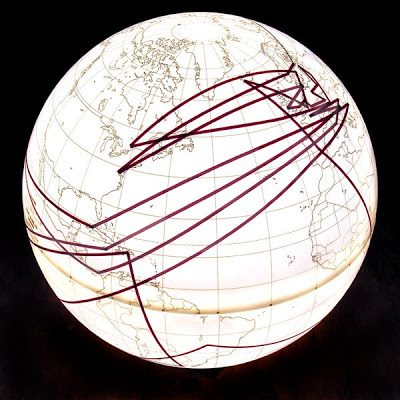













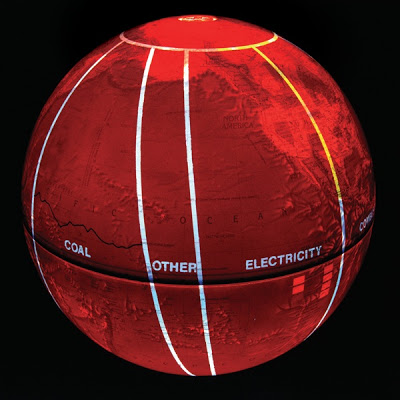 Segments originating at the South Pole (1971) represent changing proportions of fuel sources and usage up until 1996 (North Pole).
Segments originating at the South Pole (1971) represent changing proportions of fuel sources and usage up until 1996 (North Pole).
