[231-2] DNA Traces / DNA追溯, 2010
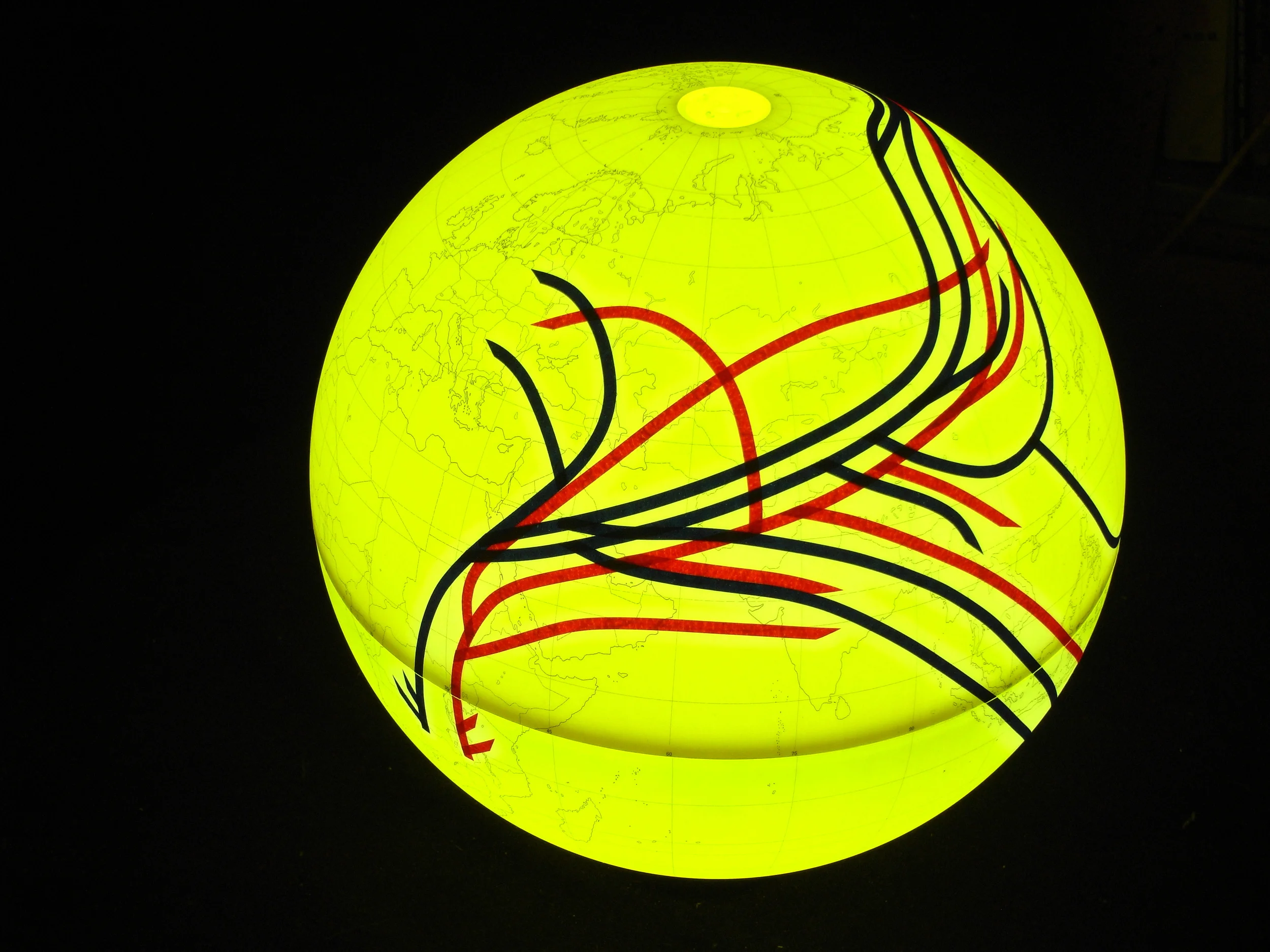
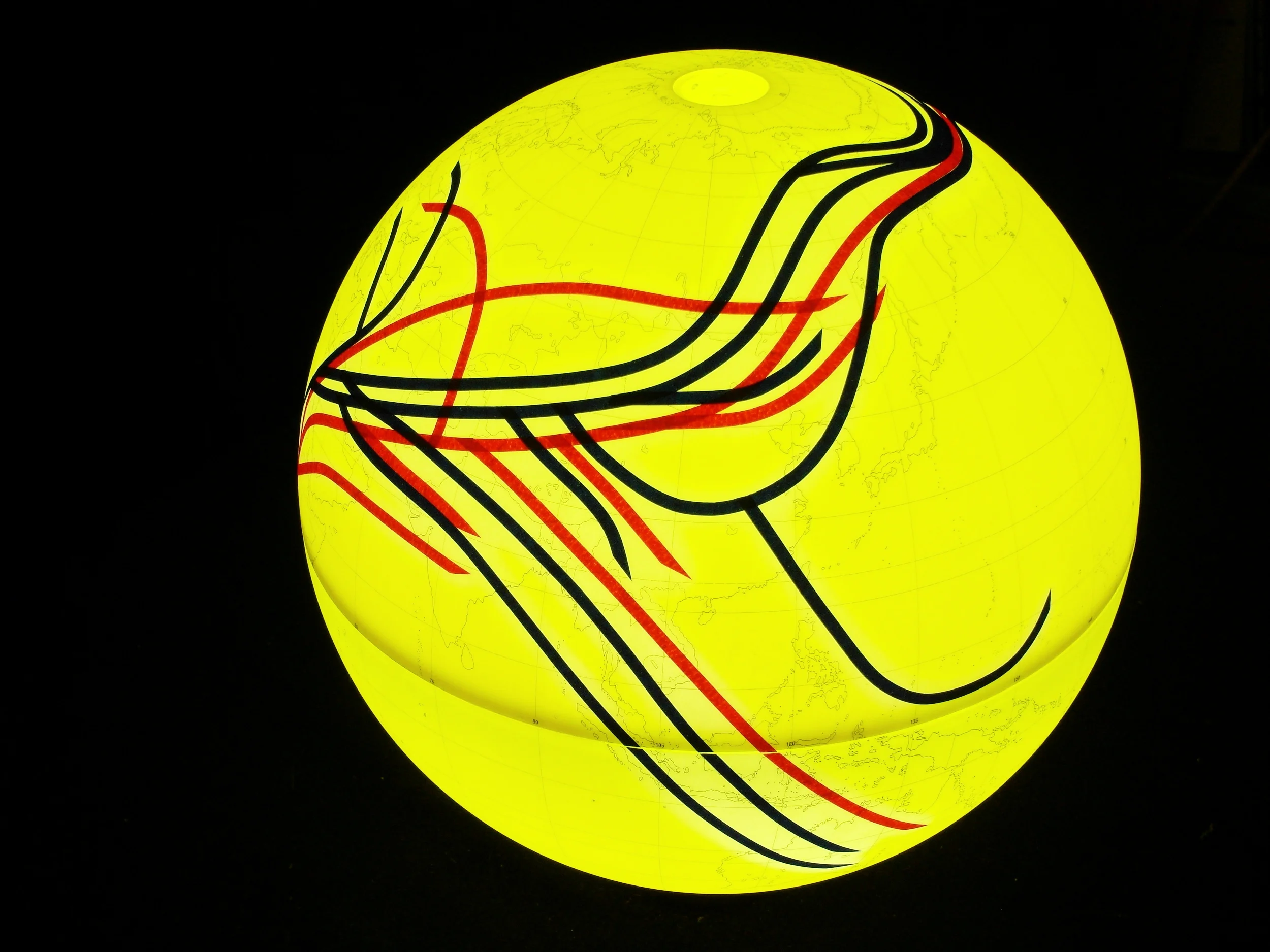
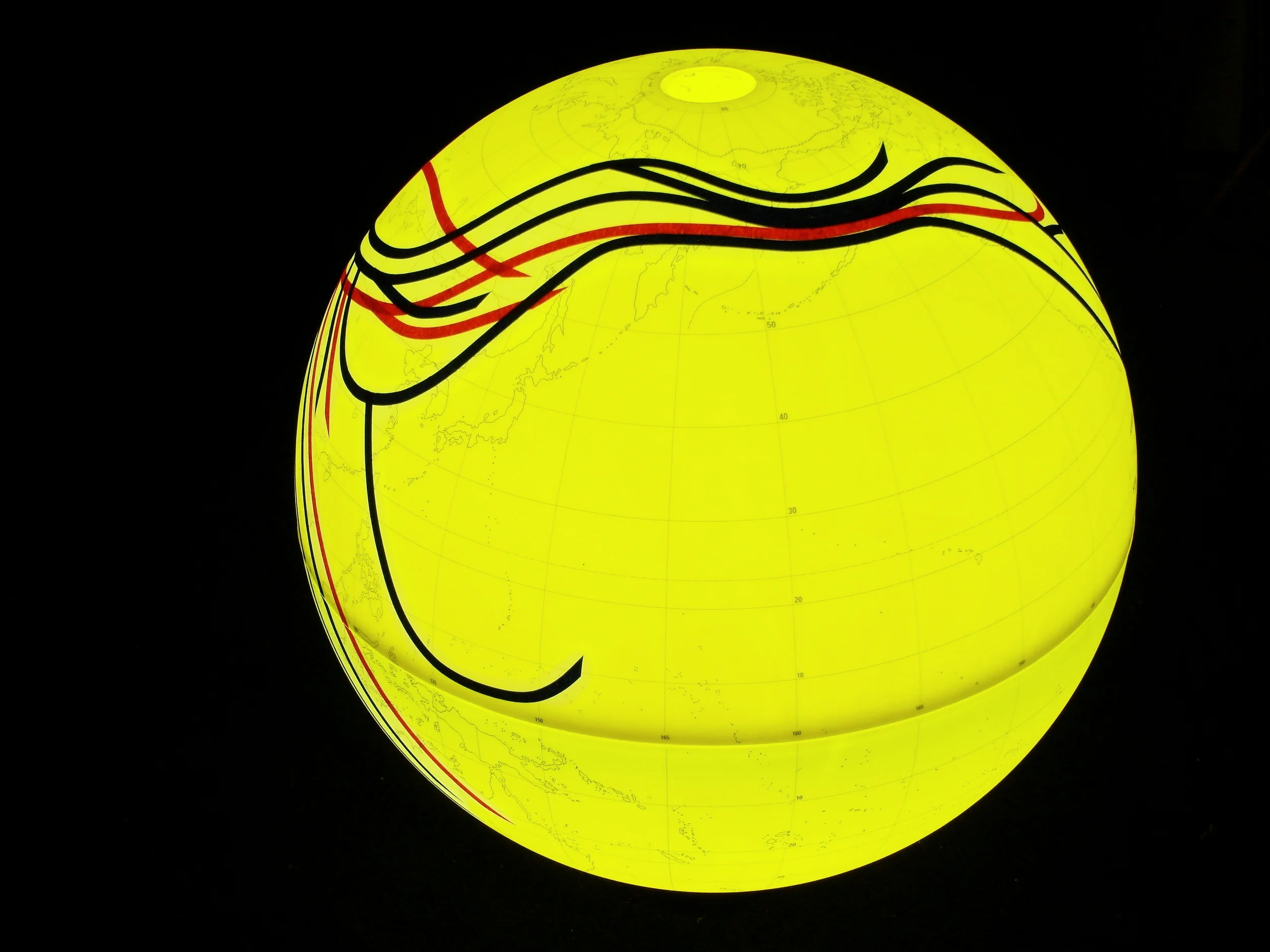
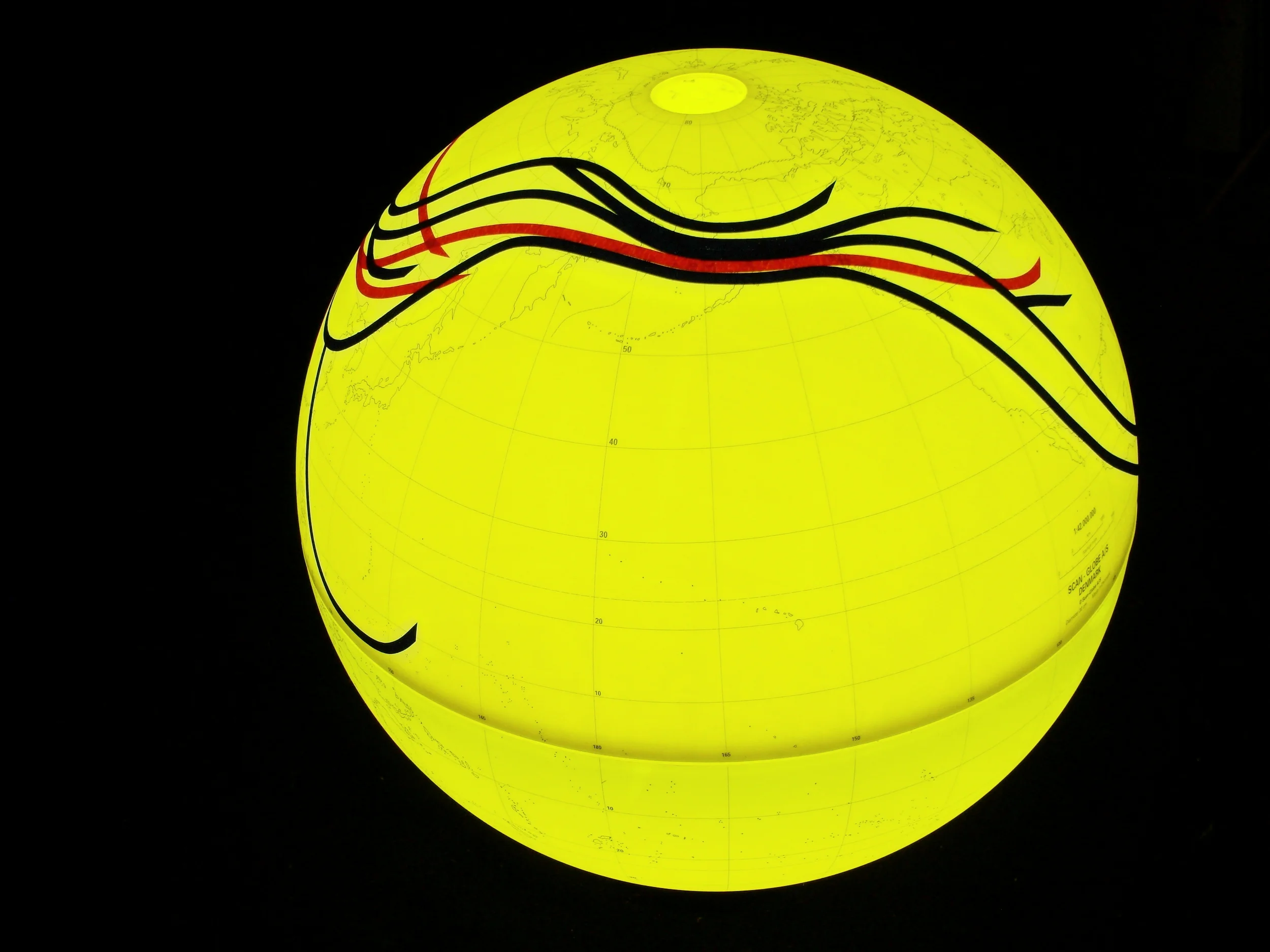
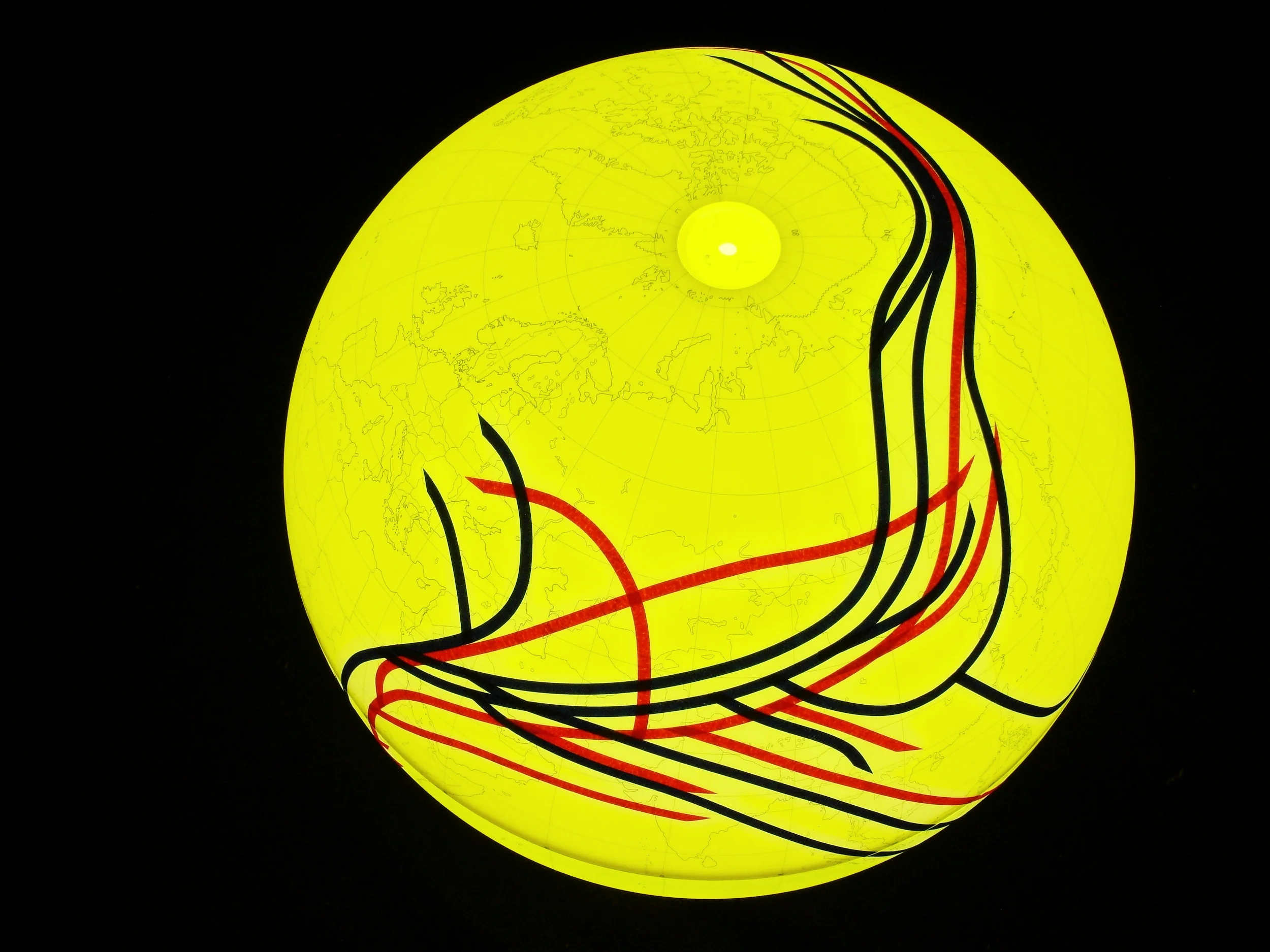
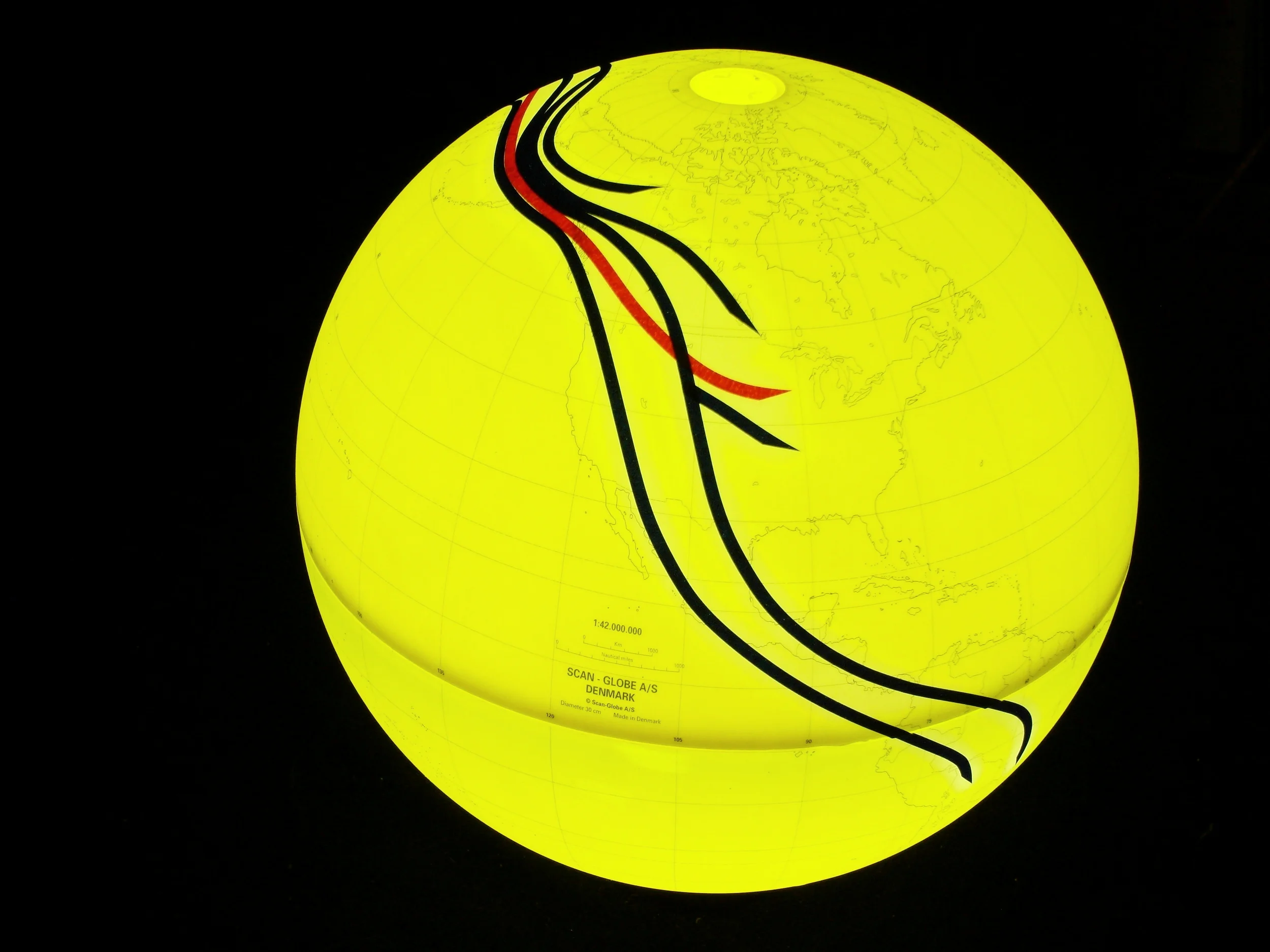
Population geneticists have traced the human family tree to an ancestral homo sapiens community of only 2000 breeding individuals living in Africa, which began splitting up approximately 144,000 years ago and migrating to Asia and Europe before the Americas. Analyses of mitochondrial DNA passed from mother to child have identified only one female (a mitochondrial “Eve”) at the root of the mDNA family tree represented by orange lines; other lineages fell extinct. Y chromosome sequences passed from father to son are represented by green lines and go back to a single chromosomal “Adam.” It is believed that 10 principle branches in the Y chromosome tree may correspond to the world’s major language groups.
人口遺傳學家將人類家譜回溯到生活在非洲有著兩千個智人祖先繁殖個體的社群,他們大約在144,000年前開始分家,往外遷徙至亞洲以及歐洲,之後到達了美洲。分析經由母系代代相承的粒線體DNA後發現,回溯粒線體DNA系譜的根源,所有族群都是一位女性的後代(「粒線體夏娃」),在此用橘色線條標示。其他人族則都已滅絕。而綠色線條用來標示著由父系代代相承到男人體內的Y染色體,追溯回到一位共同的男性,即所謂的「Y染色體亞當」。據說Y染色體樹的十個主要分支可與世界主要語系相對應。